The journey of electricity
There are several components to the electricity supply chain. The four main buckets are electricity generation, transmission, and distribution, before arriving at your home ready for you to use when you need it.
There are several components to the electricity supply chain. The four main buckets are electricity generation, transmission, and distribution, before arriving at your home ready for you to use when you need it.
Your electricity bill covers several different parts of our energy system. Each part represents an essential link in the supply chain providing electricity to your home, and the development of more sustainable, reliable and affordable electricity.
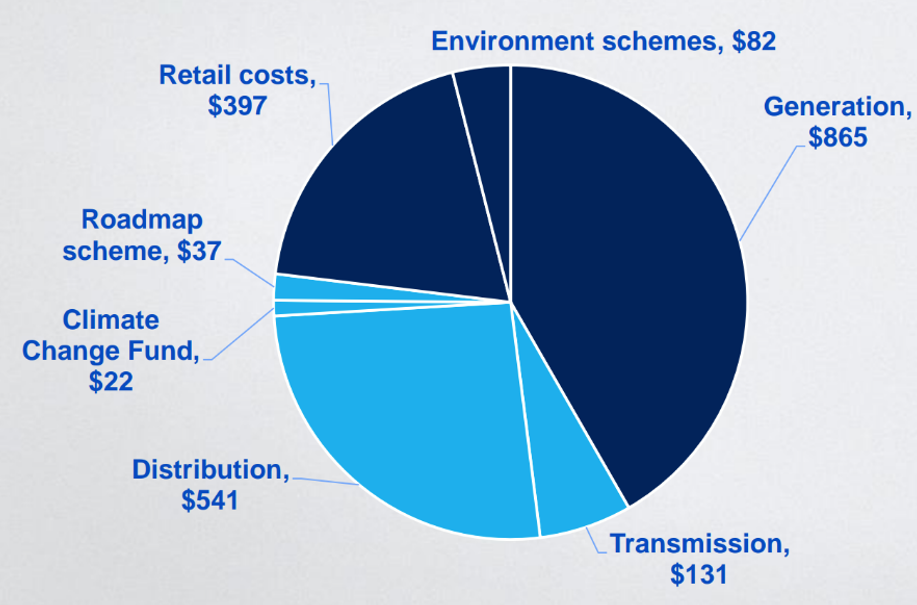
The above costs are covered in your energy bill through different charges. While electricity bills don’t all look exactly the same, here are examples of the common charges you see on your bill.
Example pricing based on AGL’s standing offer (including GST). Retail rates from 1 July 2025.
The most common types of usage charge are:
Flat rate Your electricity use is charged at a flat rate per unit of electricity used.
| Charge | Units | Rate per Unit | Amount |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flat Rate | 200kWh | $0.40 | $80 |
Peak/off-peak You pay a higher rate for using electricity in ‘peak’ hours. These are hours when there is high demand for electricity. You pay a lower rate for using electricity in ‘off-peak’ hours. This is also sometimes referred to as ‘time of use’.
| Charge | Units | Rate per Unit | Amount |
|---|---|---|---|
| Peak Usage | 100kWh | $0.65 | $65 |
| Off Peak Usage | 100kWh | $0.30 | $30 |
The usage charge that applies to you will depend on the electricity plan you have selected and the retailer you are with.
kWh (kiloWatt hour) = a unit of energy consumption. It measures the total amount of energy used in an hour.
This is a daily fixed charge, meaning that it does not vary with the amount of electricity used.
The charge applies to every day in the billing period.
| Charge | Units | Rate per Unit | Amount |
|---|---|---|---|
| Supply | 31 days | $1.09/per day | $33.79 |
For information on solar pricing visit 'Getting the most out of your solar'.
If you are looking for some extra information about energy, checkout these resources.